End-to-end differentiable molecular mechanics force field construction
/Yuanqing Wang, Josh Fass, and John D. Chodera
Chemical Science 13:12016, 2022 [DOI] [arXiv] [pytorch code] [JAX code]
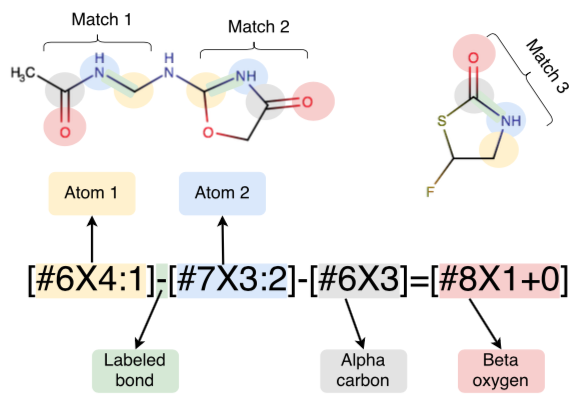
Molecular mechanics force fields have been a workhorse for computational chemistry and drug discovery. Here, we propose a new approach to force field parameterization in which graph convolutional networks are used to perceive chemical environments and assign molecular mechanics (MM) force field parameters. The entire process of chemical perception and parameter assignment is differentiable end-to-end with respect to model parameters, allowing new force fields to be easily constructed from MM or QM force fields, extended, and applied to arbitrary biomolecules.